Inhibitors of Guanine Deaminase for Hyperuricemia and Gout
Rutgers Inventor(s): Bonnie Firestein; Naomi Schlesinger; Amrik Sahota; Jacques Roberge
Awarded: August 2020
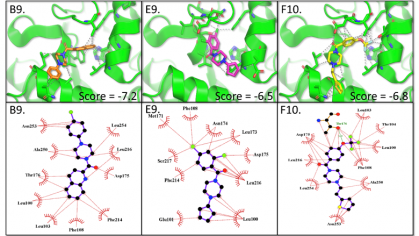
Summary: Gout is an inflammatory arthritis that results when serum uric acid (UA) levels are too high and monosodium urate (MSU) crystals deposit in and around joints and soft tissue. Gout is the most common inflammatory arthritis with a prevalence of approximately 4% among adults in the United States. Small-molecule therapeutics used to treat gout inhibit the enzyme xanthine oxidase, with the most common being allopurinol and febuxostat. However, their use may lead to hypersensitivity reactions, which can be lethal, and in fact, a Black Box warning has been issued for febuxostat. Thus, there is an urgent need for new drug targets and therapeutics for the treatment of gout. The current work targets a surprisingly overlooked but promising mechanism for the treatment of hyperuricemia in gout - the inhibition of guanine metabolism.
Market Applications:
- Treatment of patients with gout.
- Treatment of patients with hyperuricemia.
- Treatment of patients with metabolic syndrome